Table of contents
Introduction
In this post, I'll be sharing my experience in taking the Red Hat certification for Containers and Kubernetes using OpenShift Platform v4.10. The certification is different from other cloud certifications since this contains a series of hands-on tasks.
Since January of 2023, the exam (EX180) is now retired and will be replaced by Red Hat Certified Specialist in Containers (EX188).
Preparation
The most recommended learning path to prepare for this certification is to have a RedHat Learning Subscription but you can take other options like Udemy or A Cloud Guru if a learning path is available. Below is a sample screenshot of the Red Hat Learning Paths.
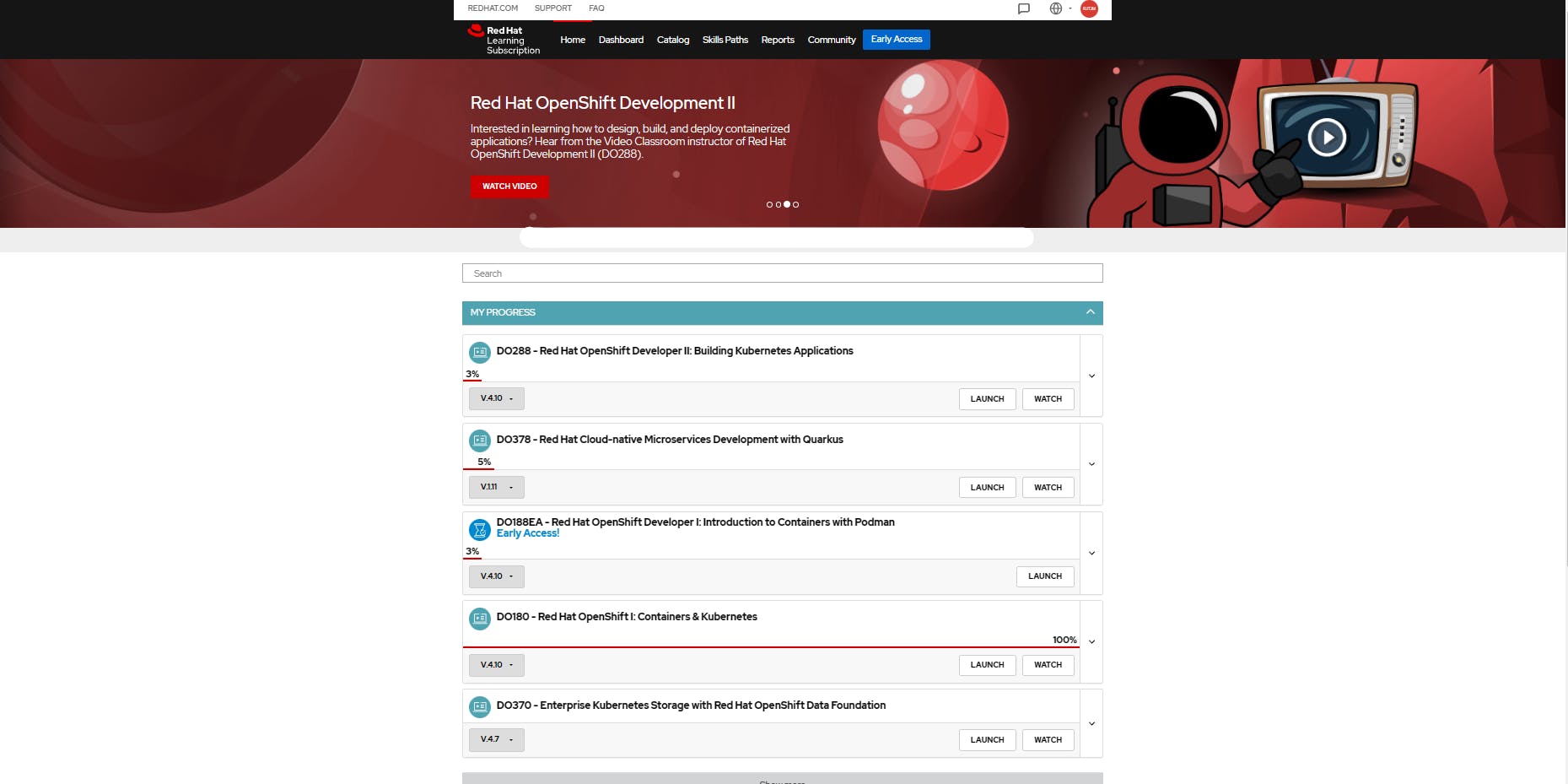
The subscription contains paths spanning from OpenShift, Camel, Kafka, Ansible, Quarkus and many more. A lab environment is given which gives you the freedom to play around using the terminal commands. The learning path for this certification is called Red Hat OpenShift I: Containers & Kubernetes (DO180). The overall effort for this module is 24 hours but it took me 1 month to prepare since I tried different Podman and OpenShift commands.
If you want to take your RedHat exam in the comfort of your home, you should read the remote exam guide. You should have a flash drive available for burning the remote exam environment ISO file.
Exam Proper
The exam consists of 8 tasks based on the objectives described here. The objectives of the new exam (EX188) can be checked here. The following EX180 objectives are.
Implement images using Podman
Manage images
Run containers locally using Podman
Basic OpenShift knowledge
Creating applications in OpenShift
Troubleshoot applications in OpenShift
The EX188 objectives are quite similar to EX180.
Implement images using Podman
Manage images
Run containers locally using Podman
Run multi-container applications with Podman
Troubleshoot containerized applications
Some tasks are dependent on each other like running multi-containers in a pod. Check an example of this here. It is expected that you have a basic understanding of Linux commands and how to modify a shell script. Below is a sample procedure on how to put a podman command in a shell script.
Running a container using Podman. Let's name it start-container.sh
#!bin/bash
# This is a sample shell script
podman run -d --name dbcontainer docker.io/mysql:latest
Running a shell script should be like this.
sh ./start-container.sh
You only have 2 hours to finish the exam. If you decided to take it in your home, be ready to have an external camera, a keyboard and mouse, an external monitor and an optional laptop docker. Every hour of the exam, the proctor will request you to scan your room using your external camera.
Tip: The exam is fond of using scripts so practice using Shell. As much as possible, read the requirements carefully. You don't want to start over again on your configurations.
Exam Results
As mentioned by Red Hat, the results will be given within 3 business days but on my end, it was sent after an hour. They will give you your score based on the percentage of each objective. The passing score is 210 over 300 which is 70%. When I took the exam, I got 249 or 83%.
After a while, Credly will issue you a badge and obtain the title: RedHat Certified Specialist in Containers and Kubernetes. For EX188, it will be RedHat Certified Specialist in Containers.
Final Thoughts
In this exam, you will learn how to use the podman and OpenShift basic commands. You will create applications inside OpenShift and how to troubleshoot. The new exam EX188 I think will be the same as EX180 with some tweaks but overall it will have the same objective of using the podman commands and deploying applications in OpenShift.

